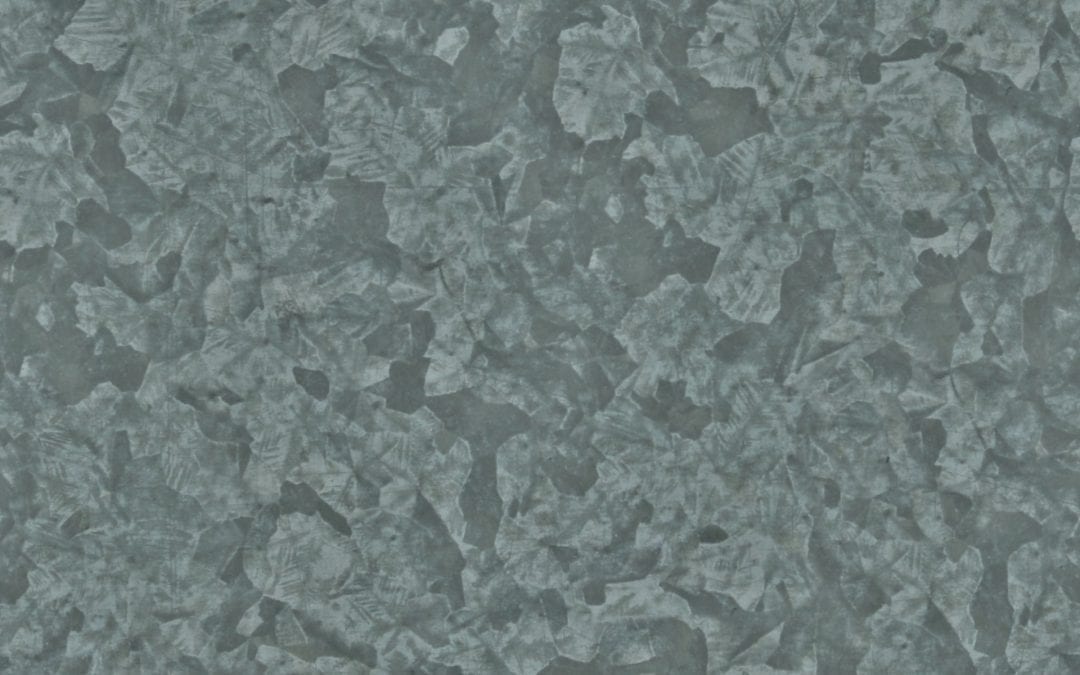
Galvanizing is a manufacturing process where steel or iron is coated with zinc. Galvanized steel, therefore, is zinc-coated steel. There are several galvanizing methods, with the most common method being hot dipped galvanization.
Benefits of Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is one of the most popular steels because it is rust-resistant and more affordable than most treated steels. And, it doesn’t require any maintenance or refinishing. Since the zinc coating protects it from the elements, the steel can last for 50 years in temperate environments. Even with severe weather exposure, galvanized steel can last for over 20 years.
Galvanizing Methods
As mentioned, there are several galvanizing methods including galvannealing, pre-galvanizing, electrogalvanizing, and hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is the most popular, which we will explain in more detail. But first, let’s briefly cover the other three.
- Galvannealing: combines hot-dip galvanizing with annealing to produce a dull matte surface that is good for welding and painting.
- Pre-galvanizing: the metal is primed with a cleaning agent and quickly passed through molten zinc which creates a more unified coating than standard hot-dipping.
- Electrogalvanizing: instead of molten zinc, the steel is covered with an electrolyte solution and then an electric current is applied which ultimately bonds the zinc to the steel.
What is the Hot Dip Galvanizing Process?
As the name suggests, the steel is dipped in hot, molten zinc. While the steel is inside the molten zinc, a metallurgical reaction occurs between the iron contained inside the steel and the hot zinc. The reaction is known as a diffusion process. The diffusion process is when the coating collects perpendicular to every surface and creates a uniform thickness.
When the steel is removed from the zinc bath, it reacts with the oxygen in the air to form zinc oxide. It then reacts to carbon dioxide and forms the final protective coating of zinc carbonate. Ultimately, the steel has a corrosion-resistant, multi-layered coating of zinc metal and iron-zinc alloy.
Hot-dipped galvanized steel has a fairly distinct appearance compared to other galvanized steel. It has a mottled, crystalline-like pattern known as a “spangle” pattern.
What is Hot Dip Galvanizing Used For?
Galvanized steel is very versatile. It is used in a wide range of industries, including agriculture, automotive, construction, solar, telecommunication, and many more. Because of its resistance to corrosion, galvanized steel is preferred in applications that may be exposed to moisture or the elements.
All kinds of screws, nuts, bolts, tools, and wires are galvanized to increase their durability. Entire steel frame buildings use galvanized steel to support the bulk of the structure. Fences, roofs, staircases, and more are often made with galvanized steel. As stated, galvanized steel is very versatile! Galvanized steel offers more than improved functionality; it also offers aesthetic appeal. Many architects incorporate galvanized steel in their designs. The shiny finish gives a clean, modern feel that is popular in contemporary architecture.
Hot Dipped Galvanized vs Galvanized Steel
In summary, hot-dipped galvanized steel is a type of galvanized steel. The hot-dip galvanizing process is relatively cheap, and the resulting product is very durable and versatile. Hot-dipped galvanized steel is most often used in applications that will be exposed to the elements as it is highly corrosion-resistant.